Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Vispy Console#
Demonstrate the use of the vispy console.
Note how the console size is independent of the canvas scaling.
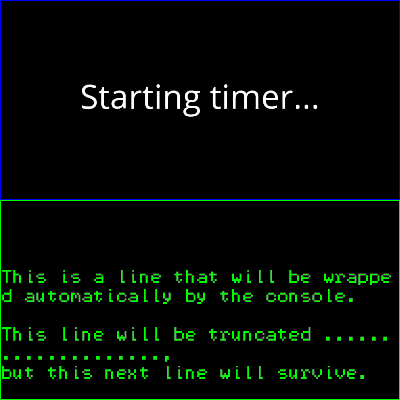
import sys
from vispy import scene, app
from vispy.scene.widgets import Console
from vispy.scene.visuals import Text
canvas = scene.SceneCanvas(keys='interactive', size=(400, 400))
grid = canvas.central_widget.add_grid()
vb = scene.widgets.ViewBox(border_color='b')
vb.camera = 'panzoom'
vb.camera.rect = -1, -1, 2, 2
grid.add_widget(vb, row=0, col=0)
text = Text('Starting timer...', color='w', font_size=24, parent=vb.scene)
console = Console(text_color='g', font_size=12., border_color='g')
grid.add_widget(console, row=1, col=0)
def on_timer(event):
text.text = 'Tick #%s' % event.iteration
if event.iteration > 1 and event.iteration % 10 == 0:
console.clear()
console.write('Elapsed:\n %s' % event.elapsed)
canvas.update()
timer = app.Timer(2.0, connect=on_timer, start=True)
console.write('This is a line that will be wrapped automatically by the '
'console.\n')
console.write('This line will be truncated ....................,\n'
'but this next line will survive.\n', wrap=False)
if __name__ == '__main__':
canvas.show()
if sys.flags.interactive != 1:
canvas.app.run()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.349 seconds)
