Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
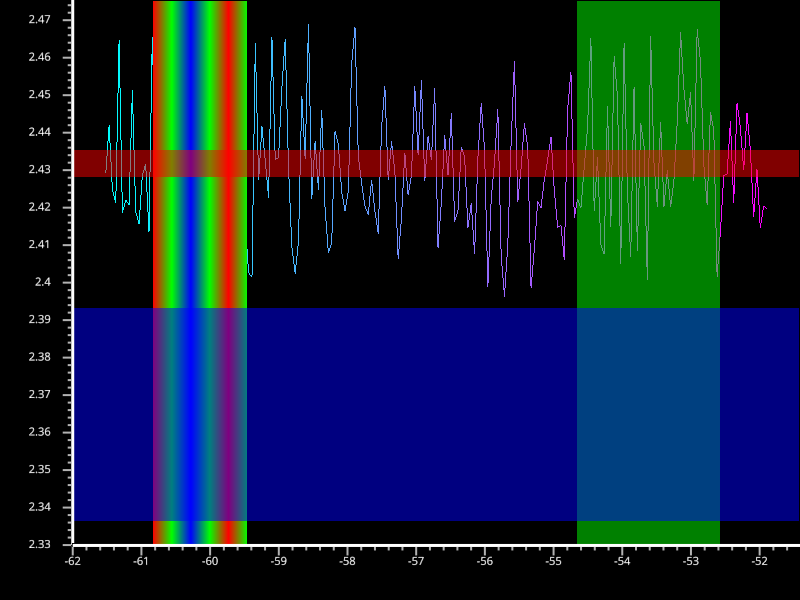
Draw an LinearRegion#
Demonstration of LinearRegion visual. Allows drawing of infinite horizontal or vertical region for 2D plots.
import sys
import numpy as np
from vispy import app, scene
# vertex positions of data to draw
N = 200
pos = np.zeros((N, 2), dtype=np.float32)
x_lim = [50., 750.]
y_lim = [-2., 2.]
pos[:, 0] = np.linspace(x_lim[0], x_lim[1], N)
pos[:, 1] = np.random.normal(size=N)
# color array
color = np.ones((N, 4), dtype=np.float32)
color[:, 0] = np.linspace(0, 1, N)
color[:, 1] = color[::-1, 0]
canvas = scene.SceneCanvas(keys='interactive', show=True)
grid = canvas.central_widget.add_grid(spacing=0)
viewbox = grid.add_view(row=0, col=1, camera='panzoom')
# add some axes
x_axis = scene.AxisWidget(orientation='bottom')
x_axis.stretch = (1, 0.1)
grid.add_widget(x_axis, row=1, col=1)
x_axis.link_view(viewbox)
y_axis = scene.AxisWidget(orientation='left')
y_axis.stretch = (0.1, 1)
grid.add_widget(y_axis, row=0, col=0)
y_axis.link_view(viewbox)
# add a line plot inside the viewbox
line = scene.Line(pos, color, parent=viewbox.scene)
# add vertical lines
color = np.array([[1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0],
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
pos = np.array([100, 120, 140, 160, 180, 200], dtype=np.float32)
vert_region1 = scene.LinearRegion(pos, color,
parent=viewbox.scene)
vert_region2 = scene.LinearRegion([549.2, 700], [0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.5],
vertical=True,
parent=viewbox.scene)
# add horizontal lines
pos = np.array([0.3, 0.0, -0.1], dtype=np.float32)
hor_region1 = scene.LinearRegion(pos, [1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5],
vertical=False,
parent=viewbox.scene)
hor_region2 = scene.LinearRegion([-5.1, -2.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.5],
vertical=False,
parent=viewbox.scene)
# auto-scale to see the whole line.
viewbox.camera.set_range()
if __name__ == '__main__' and sys.flags.interactive == 0:
app.run()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.891 seconds)
