Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Text in a Scene and ViewBox#
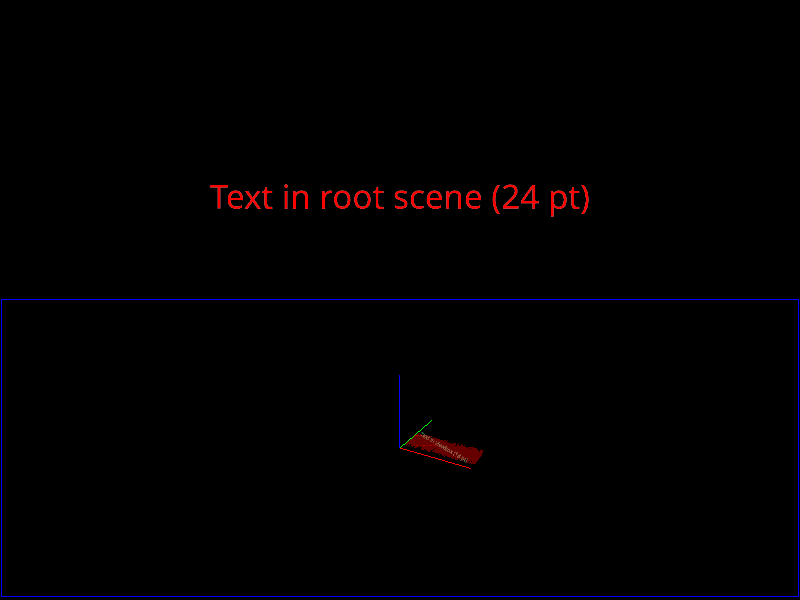
Demonstrate the use of text in the root scene and a viewbox. Note how the point size is independent of scaling of viewbox and canvas.
import sys
import numpy as np
from vispy import scene
from vispy.scene.visuals import Text
# Create canvas with a viewbox at the lower half
canvas = scene.SceneCanvas(keys='interactive')
vb = scene.widgets.ViewBox(parent=canvas.scene, border_color='b')
vb.camera = scene.TurntableCamera(elevation=30, azimuth=30, up='+z')
axis = scene.visuals.XYZAxis(parent=vb.scene)
vb.camera.rect = 0, 0, 1, 1
@canvas.events.resize.connect
def resize(event=None):
vb.pos = 1, canvas.size[1] // 2 - 1
vb.size = canvas.size[0] - 2, canvas.size[1] // 2 - 2
t1 = Text('Text in root scene (24 pt)', parent=canvas.scene, color='red')
t1.font_size = 24
t1.pos = canvas.size[0] // 2, canvas.size[1] // 3
t2 = Text('Text in viewbox (18 pt)', parent=vb.scene, color='green',
rotation=30)
t2.font_size = 18
t2.pos = 0.5, 0.3
# Add a line so you can see translate/scale of camera
N = 1000
linedata = np.empty((N, 2), np.float32)
linedata[:, 0] = np.linspace(0, 1, N)
linedata[:, 1] = np.random.uniform(0.5, 0.1, (N,))
scene.visuals.Line(pos=linedata, color='#f006', method='gl', parent=vb.scene)
if __name__ == '__main__':
canvas.show()
if sys.flags.interactive != 1:
canvas.app.run()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.399 seconds)
